BOS.Oracle: Witness and Changes
BOS.Oracle Version : v1.0.0
Overview
In the real world, the seller won't sell out the products until the payment is surely received, and the buyer won't buy the products until the authenticity is verified. "Credit" is the most fundamental condition for deals in reality, which means that we are unable to complete the deal if there is no trust between the buyer and the seller. However, it is so hard for us to reach trust that we can only make decisions relying on the credit of both parties of the transaction (which is essentially relying on the previous transaction history to make probabilistic estimation) or depending on a trusted third party (If it is really credible, and where does the basis of trust come from?). It makes us take more risks and expend more energy and resources in the complicated present situation. How to solve the problem? If it is feasible to settle it by combining blockchain technology? We developed BOS Oracle Service with an expect of connecting the data of blockchain and reality as a bridge.
Some Oracle services are designed on the basis of the assumption of a dependable or authoritative data source, which is theoretically too risky to guarantee the authenticity of the data provided by such a data source. Thus, the principle of the BOS Oracle system from the beginning is that:
BOS Oracle does not rely on each oracle provider's 100% credibility of the data they provided.
BOS Oracle treats each oracle provider as a participant in the game, in order to achieve overall credibility in the game.In this way, we are able to not only get the credibility of the input data of blockchain, but also export "trust" to the real world. In fact, it seems a reliable platform based on the blockchain that presents its service in the form of prophecy. BOS Oracle will extend the value of blockchain from its monetary attributes to the construction of transactions and rules. This extension should solve or improve many trust issues of reality, so as to expand the application boundary of blockchain. And finally it enables blockchain technology to land on the scene other than transaction and transfer.
Characteristics
Game Completion
The whole Oracle system is constructed on Game Theory. We abstract the roles involved in the Oracle, and call the roles providing data or services as data providers and the roles consuming data as data consumers. In the meanwhile, we also introduce the role of arbitrator to complete the construction of the whole game model.
When using a data service provided by an Oracle, anyone has the right to prosecute and lodge an appeal. If he/she refuses to accept the verdict, there will be several rounds of arbitration, and the system will punish the perpetrator of the final judgment. The whole system will form the game balance of "data providers", "data user" and "arbitrator", and the whole game process and rule making can guarantee justice is an event with great probability.
Positive Incentive
The game model of BOS Oracle may construct the “Prisoner's Dilemma” between the data providers, provide the victim with the power to appeal, and make the fair judgment of arbitrators order. Anyway, for the rational participants system rules are static and foreseeable, thus being honest and fair to participate is its superior strategy, while for the irrational ones, who may be punished with great probability, thereby the whole prophecy service will run positively, healthily and efficiently.
Full scene coverage
During the construction of BOS Oracle, we fully realized the complexity, irregularity, fragmentation, and privacy of real-world data. From publicly available data (such as weather report) to restricted data (such as personal credit information), it can be used as an Oracle service of BOS. Any data service which may described and identified in a sense by BOS Oracle to provide service in manners of contract tables, contract actions, offchian callbacks ect.
Composition
Staking Model
Staking model is the core of the BOS Oracle System. It adopts the accountability trigger mechanism to build the system. The system, was built relying on the use of accountability trigger mechanism by the Staking model, in which the data provider, arbitrator and complainant all need mortgage Token. As the anchor of punishment and reward, mortgage is the basis of positive incentive of the system. When the participant is judged by the system as doing unfair things, the corresponding informant and impartial arbitrator will get the corresponding mortgage as reward.
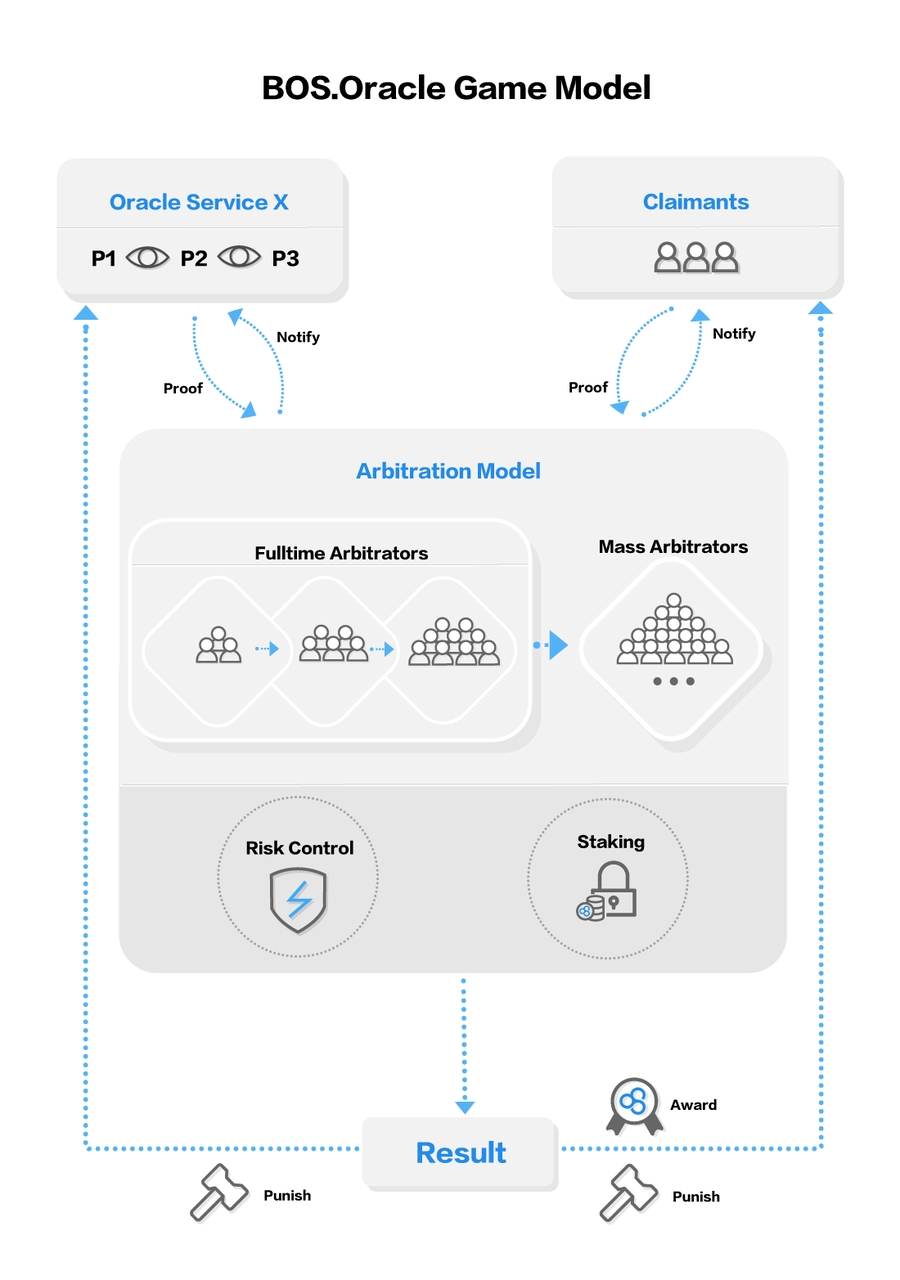
Arbitration Model
Arbitration is the source of system fairness. To avoid the achievement of bribery, the system applies a plan for multiple rounds of arbitration, in which the number of arbitrators in each round increases step by step. With the expansion of arbitrators, it will become more and more difficult to pay bribes, and the cost will increase sharply, which will eventually lead to the failure of bribery.
The arbitration model of BOS Oracle will be divided into two phases:
The "Fulltime Arbitrators" phase, 21 arbitrators in total who must be timely response to the arbitration cases; in this stage, a total of 3 rounds of arbitration can be conducted, with 3, 5 and 9 persons in each round and no repetition in each round;
The "Mass Arbitrators” phase, the participants in the entire Oracle service will be involved in. Extensive arbitration and random sampling will be conducted, subject to the majority; The number of "Mass Arbitrators" will be well regulated, in case of "Sybil Attack".
Intelligent Risk Control
In order to ensure maximum security, “intelligent risk control” can always assure that the data provider has enough mortgage Token to be locked for punishment. Its main logic is used that players based on Oracle service DApp transfer Token directly to the “intelligent risk control” account rather than DApp project accounts, when someone on the Oracle service initiated arbitration, “intelligent risk control” will base on the information (such as history of the data provider behavior and the current expenditure information) to intelligently calculate capital of freezing and thawing cycle time. If there is no exception in the whole process, the DApp project party can normally extract Token from the “intelligent risk control” account.
“Intelligent risk control” is an option, depending one the DApp's clients application. However, from the perspective of market competition, DApp which provides more guarantee for users will be preferred.
Data State
Regarding the variety and complexity of date, the system provides multiple data interactions for convenient use. Overall, the data can be exerted in the following four ways:
1. The data provider writes the data to the chain and the user reads it
2. The data provider listens for and invokes events and actively pushes data to the user on the chain
3. The data provider listens for and invokes events and actively pushes data to the user off chain
4. The data interaction is completed off chain, and the signature ensures the data reliable
4.1 Interactive process of data off chain
Documents
Last updated
Was this helpful?